ADVERTS
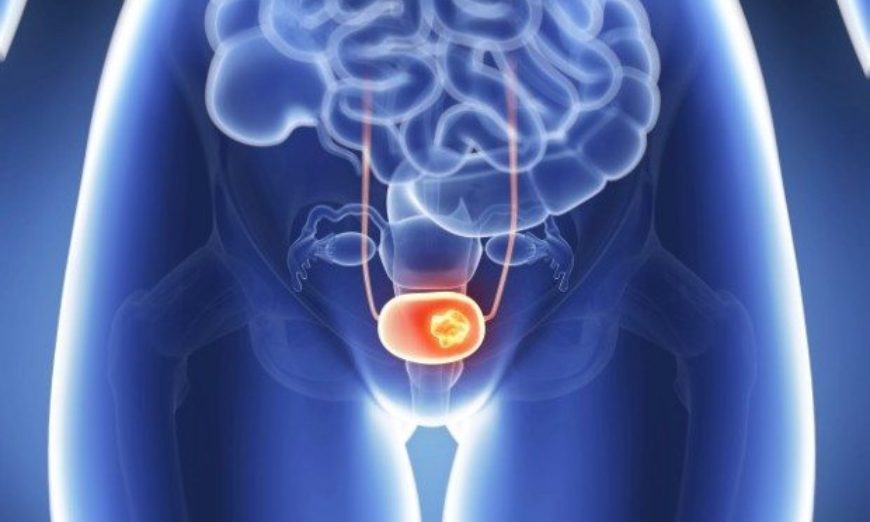
It is a tumor that originates in the cells that cover the bladder from the inside, that is, the one that is in direct contact with urine.
It is a tumor considered rare and mainly affects men. In general, toxic substances that are eliminated in the urine are important factors in the development of cancer and smoking is one of the main causes of the tumor.
ADVERTS
The bladder stores urine formed by the kidneys and releases it when you feel like it.
Bladder cancer begins in the inner lining of the organ, made up of cells called urothelial cells. Most of the time, the tumor is born in these cells and grows into the bladder, where urine is stored. However, when it is not discovered early, the tumor can grow to the point of penetrating the bladder muscle. In this case, the chance of the tumor spreading throughout the body is greater.
In more serious cases, the tumor may have already grown too much and penetrate organs and parts of the body that are around the bladder.
Symptoms
ADVERTS
Common symptoms of bladder cancer include: bright blood or reddish color in the urine, pain in the lower abdomen or discomfort when urinating, the urge to urinate several times a day and a feeling of trapped urine. However, they are not definitive signs of bladder cancer, other diseases may be causing these symptoms.
However, anyone experiencing these symptoms should see a doctor.
What exams are done
A doctor's assessment is essential. Knowing the symptoms and signs of the disease that began and progressed, he or she can perform a physical examination and order the necessary tests to obtain the diagnosis.
These tests may include: laboratory tests of blood, urine and cystoscopy (an exam that looks at the bladder from the inside and can see what is wrong).
The main treatments for bladder cancer are: surgery, radiotherapy, immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Based on the stage of the cancer, the doctor will choose between one or more of these treatments.
