ADVERTS
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Composed of two layers: the epidermis, on the outside, and the dermis, on the inside. It regulates body temperature and serves as protection against external agents, such as: sunlight, heat, infectious agents and chemical agents (arsenic ingestion, exposure to X-rays and radio).
Skin cancer is very common in Brazil, corresponding to 25% of diagnosed malignant tumors, and the majority occur due to excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun.
ADVERTS
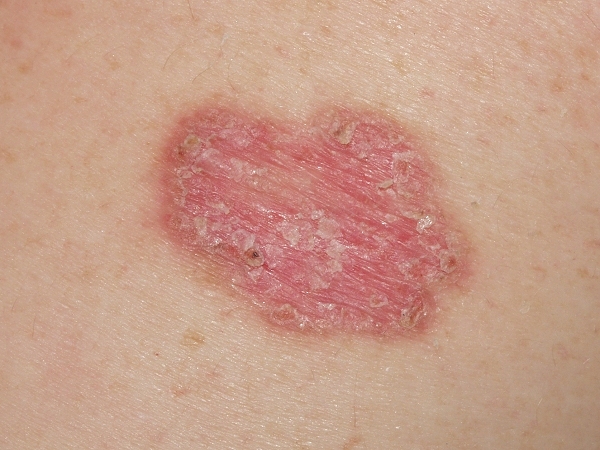
Type of skin cancer
They can be of different types. The most common are carcinomas (basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma) with a higher incidence, but less severity. Melanomas, which are less common, are more serious due to the increased risk of metastases.
People who have a family history of the disease, with light skin and eyes, blond or red hair, albinos, those who are exposed to the sun and chemical agents excessively and have many moles, form the population most at risk for developing the disease.
The malignant lesion is usually pink, reddish or dark, and presents slow but progressive growth. It may look like a wound that does not heal, or moles that grow slowly, but are itchy, bleed or have changes in color, consistency and size (generally larger than 6 mm). Other characteristics are asymmetry and irregular edges. The type of tumor is less important than its size at the time of diagnosis in determining treatment and prognosis.
ADVERTS
A person should see a doctor whenever they notice a new lesion on the skin or when an old lesion undergoes some type of change.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made through the clinical appearance of the lesion, its color and shape and the results of the biopsy of the tissues of the lesion itself and those surrounding it. Early diagnosis is very important, as the chances of a cure are greater.
Treatment
Treatment consists of surgical removal of the lesion and surrounding tissue. Chemotherapy or radiotherapy are resources used in the most serious cases.
Some tips: Carry out a skin self-examination regularly and observe whether there are any blemishes, lesions, wounds, signs or moles that are new or have changed. Do not forget to examine the palms of your hands, the spaces between your fingers, the soles of your feet and your scalp; Avoid excessive exposure to the sun between 10 am and 3 pm; Use sunscreen with appropriate protection for your skin type, as well as a hat and clothing to protect yourself; Avoid sunburns, especially during childhood and adolescence; Do not exaggerate exposure inside tanning beds, as they also emit ultraviolet rays; See a dermatologist regularly, especially those who have fair skin, which turns red easily when exposed to the sun, and/or a family history of skin cancer.
