ADVERTS
O mieloma múltiplo é um câncer das células plasmáticas da medula óssea. As células plasmáticas são responsáveis por ajudar o corpo a combater infecções, produzindo proteínas chamadas anticorpos.
In multiple myeloma, plasma cells grow uncontrollably in the bone marrow and form tumors in areas of solid bone.
ADVERTS
The growth of these tumors makes it difficult for the bone marrow to produce healthy red blood cells and platelets. Multiple myeloma mainly affects older adults.
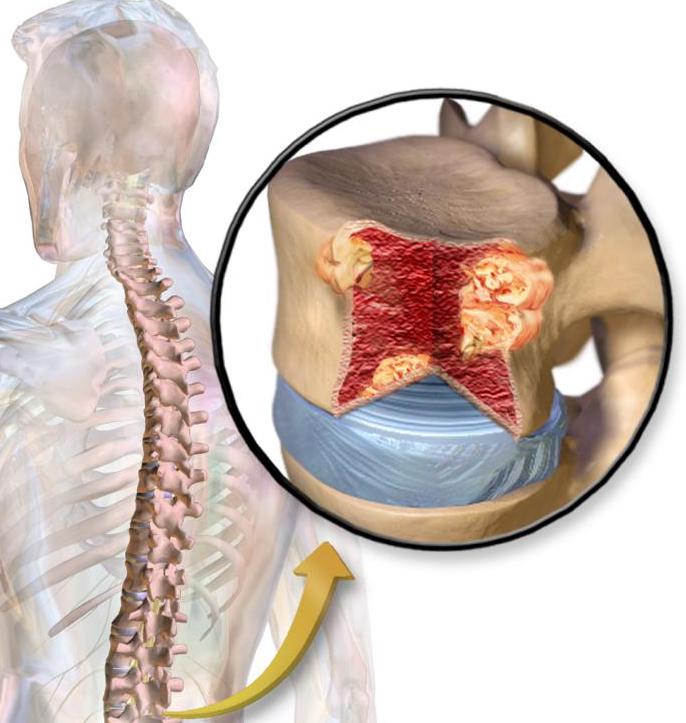
Exams
Blood tests help in diagnosing the disease. These may include: blood tests to check calcium levels, total protein and kidney function; complete blood count; blood and urine tests to identify proteins or antibodies (immunofixation); blood tests to quickly and accurately measure the specific level of certain proteins called immunoglobulins (nephelometry).
An X-ray may show fractures or hollow areas within bones. A bone marrow biopsy may also be performed. A bone densitometry can show bone loss.
Symptoms
ADVERTS
Multiple myeloma causes anemia (makes a person more likely to have infections and abnormal bleeding). Bone or back pain may occur, often in the ribs or back. If the bones of the spine are affected, it results in numbness or weakness in the arms or legs.
Other symptoms include: bleeding problems; fatigue due to anemia; fever without any other cause; difficulty breathing due to anemia; unexplained bone fractures.
Treatment
In treatment, the objective is to alleviate symptoms, avoid complications and prolong life.
In some cases, people have a slow-developing type of multiple myeloma, which takes a few years for symptoms to appear.
Medications for treatment purposes include: Dexamethasone, melphalan, cyclophosphamide, doxil, thalidomide, lenalidomide (Revlimid) and bortezomib (Velcade), which can be used together or separately; Bisphosphonates (pamidronate), to reduce bone pain and prevent fractures.
Radiation therapy is used to relieve bone pain or treat a bone tumor.
Two types of bone marrow transplantation can be tried: Bone marrow or stem cell autotransplantation: uses the patient's own stem cells. In younger patients, this increases the survival rate and; allotransplantation: uses stem cells from another person. It involves serious risks, but offers the possibility of a cure.
People with multiple myeloma should drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration and help maintain adequate kidney function. They should be careful when taking X-ray exams that use contrast.
